
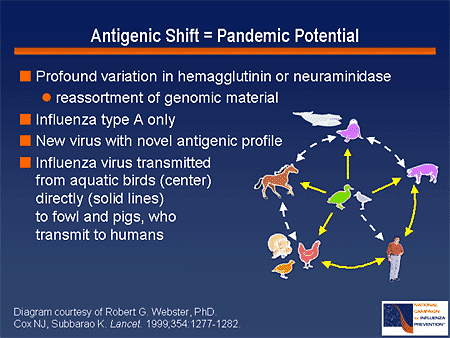
Therefore, the mutations of these H and N coding genes allow the viral particles to escape from the host immune systems and spread the disease.Īntigenic drift in epidemic flues such as H3N2 and the viral strains are capable of infecting new individuals of the same host species to spread the disease easily. As a result of this point mutation, viral particles acquire the capability of changing the H and N antigen structures which cannot be recognized by the host cell antibodies or vaccines. It happens due to gradual development and accumulation of a point mutation in the genes of H and N. Antigenic drift is such kind of a genetic variation common in influenza virus. However several genetic variations of influenza viral particles limit the chance of destroying the viral antigens which enter the host body by the host immune system. H and N antigen structures can be easily recognized by the host defense systems which destroy the viral particles to prevent the disease occurrence. H and N antigens of the influenza virus bind to the host cell receptors and make a successful infection to cause the disease. It exists in different strains and has a segmented RNA genome, and two prominent antigens (receptors) called H and N on the glycoprotein coat. Influenza virus is one type of virus responsible for the common cold associated diseases among humans and other animals.

Viral genome codes glycoproteins ( antigens) which are important for attaching to the host organism and include viral genome to replicate within the host organism. They are composed of genetic material and glycoprotein capsid. Viruses are electron microscopic small infectious particles which can infect all forms of living organisms including bacteria and plants. Side by Side Comparison – Antigenic Drift vs Antigenic Shift Both these variations help the influenza virus to overcome host defenses.Ĥ. The key difference between antigenic drift and antigenic shift is that antigenic drift is a genetic variation that occurs in the antigen structures due to a point mutation happens in the genes of the H and M within the viral genome over the year whereas antigenic shift is a variation occurs in the antigenic structures due to a sudden genetic reassortment between two or more closely related influenza viral strains. Main two types of glycoproteins (antigens) named hemagglutinin (H) and neuraminidase (N) located at the outer surface of the virus are modified by the viral genes as a result of antigenic drift or antigenic shift. These variations make it difficult to prevent common diseases associated with influenza virus by vaccines or the natural immunity system. Antigenic shift and antigenic drift are two types of genetic variations that occur in influenza virus. The antigenic structures of the influenza virus change its shape to a new shape which cannot be recognized by the antibodies.
Key Difference – Antigenic Drift vs Antigenic Shift


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
